Objective 9: Supply and Demand
The interaction of supply and demand in a market economy determines price.
|
| Definition | Laws | Determinants | Equilibrium |
Demand | Willingness and ability to buy various quantities of a good or service at various prices | Law of Demand: Quantity demanded varies inversely to price. If all else remains equal, the lower the price, the higher the quantity demanded, and the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded. | Factors other than price influencing demand: substitutes, complements, number of demanders, consumer preference, income
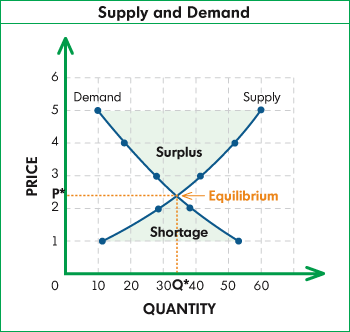
| Equilibrium is the point where supply and demand balance each other; below this point is a shortage, and above this point is a surplus. |
Supply | Willingness and ability to provide various quantities of a good or service at various prices | Law of Supply: Quantity supplied varies directly with price. If all else remains equal, the lower the price, the lower the quantity supplied, and the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. | Factors other than price influencing supply: number of producers, technology, government policies, productivity of resources | Equilibrium is the point where supply and demand balance each other; below this point is a shortage, and above this point is a surplus. |
Let's take another look at the following video (you viewed this earlier in the section Overview). It is short but provides a lot of information in that short time. Before you watched it to just get the gist, so you will want to watch it for understanding this time.
Show what you know!