Average Velocity and Instantaneous Velocity
If the velocity is not the same from an initial point in time to a final point in time of the motion the velocity is not uniform. In this case, one has to use average velocity to describe the motion.
Average Velocity is defined as the ratio of total displacement in a given time interval.
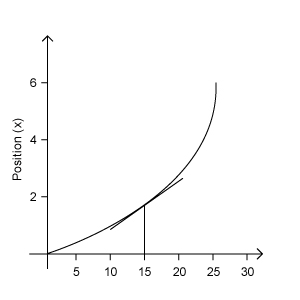
- Consider an object has different velocities at different instances of time. Then you have to use average velocity as explained above. In this case, the position-time graph will be a curve (or not a straight line) as shown below.
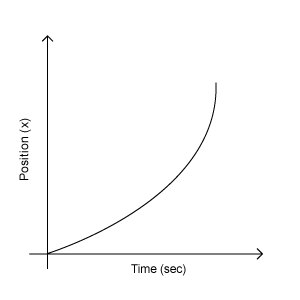
What is the velocity of that object at any particular instant of time? Is this velocity different from the average velocity? YES!
The Instantaneous Velocity is the velocity at any instant of time and it is defined as the ratio of displacement in a given time interval within which the change of displacement is constant.
- The instantaneous velocity at any point of time can be found by finding the slope of the tangent at that time on the Position-time graph.