Acceleration and Average Acceleration
From the previous example, we can conclude that the rate of change of velocity at any given time interval is called acceleration.
The change of velocity is not always the same at different intervals of time, so one has to use average acceleration. This can be understood using the following example.
A child is running straight from one pole to another in a shopping complex. According to the graph below, we can see that her acceleration is not constant and we have to use average acceleration to describe the motion between the initial and final points of the motion. Average acceleration is the total change in velocity of the object in a time interval. The change of velocity in this time interval does not have to be uniform.
The S.I unit of acceleration is m/s2.
The formula for average acceleration can be found out by using the velocity-time graph:
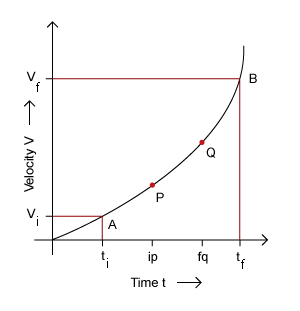
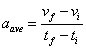
The above equation represents the average acceleration between the points A and B in the graph. Note that the change of velocity is not uniform between points A and B.
a = 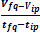
The above equation represents the acceleration between the points P and Q in the graph. Note that the change of velocity is almost uniform between the points P and Q.
The reduction of time interval further between the points P and Q shows instantaneous velocity.