Newton’s Third Law
Newton’s Third Law
You've probably heard Newton’s Third Law stated simply, "For every action there is an opposite and equal reaction." A better interpretation of the law states that for every force, there is an equal and opposing force.
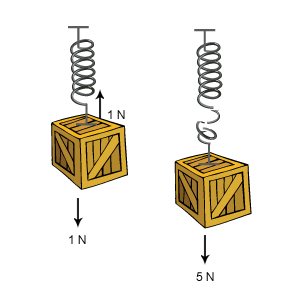
For example, if you put a 1 N force on the spring downward, there is 1 N force upward as shown. What happens if you apply a 10 N force? You may never get beyond 5 N when the spring cannot supply a reaction, so it breaks.
The animation below shows Newton’s Third Law and how forces act in pairs. In this case, the bird’s wings apply a force on the air and the air applies a force on the wing. This is called an action reaction pair. Note that the force on the wing is also equivalent to the force of the bird’s weight, keeping it from falling out of the sky. This, however, is not the action-reaction pair.