Frictional Force
Frictional Force is a force which opposes the motion or tends to oppose the motion. There are two types of frictional forces:
- Static friction
- Kinetic friction
Static friction is the resistive force that operates between the two surfaces which are in contact but remain at rest.
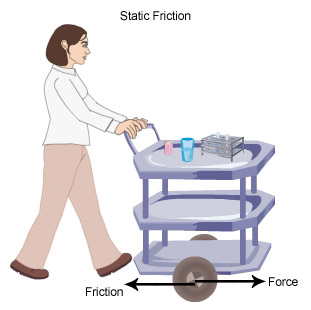
You can see from the above picture that the cart is at rest though a force is acting on it. This is because it is balanced by the frictional force on the wheels.
Static friction can be calculated using the following formula:
Fs = μs N
N = Normal force = m g
μs = coefficient of Static friction
What happens to the cart when the applied force becomes greater than the frictional force? Watch the animation below.
The trolley moves because there is a net force that acts on the trolley.
Net force = force applied – frictional force
Therefore, the kinetic friction is the resistive force that operates between the two surfaces where there is motion.
Kinetic friction can be calculated using the following formula:
Fk = μk N
N = Normal force = m g
μk = coefficient of Kinetic friction.